3. KRI Specification
The objective of this section is to introduce the KRI specification - the technology building blocks, overall architecture, standards used, query languages and inference rules. It describes how to modify the KRI, how to change the default underlying ontology and database, and how to adjust the inference rule-set of the OWLIM semantic repository.
A demo of the KRI is running on http://molto.ontotext.com.
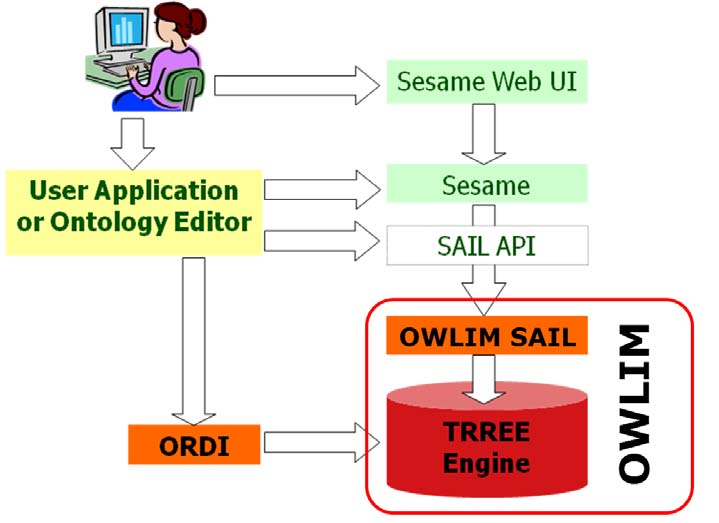
The KRI is responsible for the storage and retrieval of content metadata, background knowledge, upper-level ontology, and other possible data, if available (users and communities), and exposes convenient methods for interoperability between the stored knowledge and the toolkit for rendering natural language to machine readable semantic models (ontologies) and vice versa.
The KRI includes:
- OWLIM — a semantic repository that stores all structured data such as ontologies, background knowledge, etc., and provides SPARQL query mechanism and reasoning.
For more details about the OWLIM architecture and function, please see the OWLIM section. - RDFDB — an API that provides a remote access to the stored structured data via JMS.
For more details about the RDFDB architecture and function, please see the RDFDB section. - PROTON Ontology — a light-weight upper-level ontology, which defines about 300 classes and 100 properties, covering most of the upper-level concepts, necessary for semantic annotation, indexing and retrieval.
- KRI Web UI — a UI that accesses OWLIM through the RDFDB layer. The web UI gives the user the possibility to browse the ontologies and the database, to execute SPARQL queries, etc.
For more details about the KRI Web UI, please see the KRI Web UI section.
3.1 OWLIM
The major component of the KRI is OWLIM - a semantic repository, based on full materialization and providing support for a fraction of OWL. It is implemented in Java and packaged as a database in Storage and Inference Layer (SAIL) for the Sesame RDF database. Following is a detailed description of its architecture and supported semantics.
3.1.1 Overview
Semantic Repositories are tools that combine the characteristics of database management systems (DBMS) and inference engines. Their major functionality is to support efficient storage, querying and management of structured data. One major difference to DBMS is that Semantic Repositories work with generic physical data models (e.g. graphs). This allows them to easily adopt updates and extensions in the schemata, i.e. in the structure of the data. Another difference is that Semantic Repositories use ontologies as semantic schemata, which allows them to automatically reason about the data.
The two principle strategies for rule-based reasoning are:
- Forward-chaining: to start from the known facts and to perform inference in an inductive fashion. The goals of such reasoning can vary: to answer a particular query or to infer a particular sort of knowledge (e.g. the class taxonomy).
- Backward-chaining: to start from a particular fact or a query and to verify it or get all possible results, using deductive reasoning. In essence, the reasoner decomposes (or transforms) the query (or the fact) into simpler (or alternative) facts, which are available in the KB or can be proven through further recursive transformations.
Imagine a repository, which performs total forward-chaining, i.e. it tries to make sure that after each update to the KB, the inferred closure is computed and made available for query evaluation or retrieval. This strategy is generally known as materialization.
3.1.2 Sesame
Sesame is a framework for storing, querying and reasoning with RDF data. It is implemented in Java as an open source project by Aduna and includes various storage back-ends (memory, file, database), query languages, reasoners and client-server protocols.
There are essentially two ways to use Sesame:
- as a standalone server;
- embedded in an application as a Java library.
Sesame supports the W3Cs SPARQL query language and Adunas own query language SeRQL. It also supports most popular RDF file formats and query result formats. Sesame offers a JBDC-like user API, streamlined system APIs and a RESTful HTTP interface. Various extensions are available or are being developed by third parties. From version 2.0 onwards, Sesame requires a Java 1.5 virtual machine. All APIs use Java 5 features such as typed collections and iterators. Sesame version 2.1 added support for storing RDF data in relational databases. The supported relational databases are MySQL, PostgreSQL, MS SQL Server, and Oracle. As of version 2.2, Sesame also includes support for Mulgara (a native RDF database).
Sesame Architecture
A schematic representation of Sesame's architecture is shown in Figure 1 below. Following is a brief overview of the main components.
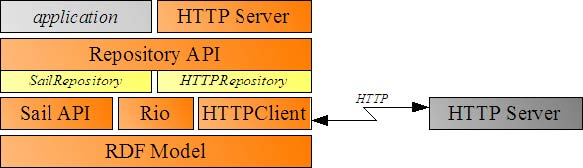
Figure 1 - Sesame Architecture
The Sesame framework is as a loosely coupled set of components, where alternative implementations can be exchanged easily. Sesame comes with a variety of Storage And Inference Layer (SAIL) implementations that a user can select for the desired behavior (in memory storage, file-system, relational database, etc). OWLIM is a plug-in SAIL component for the Sesame framework.
Applications will normally communicate with Sesame through the Repository API. This provides a high enough level of abstraction so that the details of particular underlying components remain hidden, i.e. different components can be swapped in without requiring modification of the application.
The Repository API has several implementations, one of which uses HTTP to communicate with a remote repository that exposes the Repository API via HTTP.
The SAIL API and OWLIM
The SAIL API is a set of Java interfaces that support the storage and retrieval of RDF statements. The main characteristics of the SAIL API are:
- It is the basic interface for storing/retrieving/deleting RDF data;
- It is used to abstract from the actual storage mechanism, e.g. an implementation can use relational databases, file systems, in-memory storage, etc;
- It is flexible enough to support small and simple implementations, but also offers sufficient freedom for optimizations that huge amounts of data can be handled efficiently on enterprise-level machines;
- It is extendable to other RDF-based languages;
- It supports stacking of SAILs, where the SAIL at the top can perform some action when the modules make calls to it, and then forward these calls to the SAIL beneath it. This process continues until one of the SAILs finally handles the actual retrieval request, propagating the result back up again;
- It handles concurrency and takes care of read and write locks on repositories. This setup allows for supporting concurrency control for any type of repository.
Other proposals for RDF APIs are currently under development. The most prominent of these are the Jena toolkit and the Redland Application Framework. The SAIL shares many characteristics with both approaches, however an important difference between these two proposals and SAIL, is that the SAIL API specifically deals with RDFS on the retrieval side: it offers methods for querying class and property subsumption, and domain and range restrictions. In contrast, both Jena and Redland focus exclusively on the RDF triple set, leaving interpretation of these triples to the user application. In SAIL, these RDFS inferencing tasks are handled internally. The main reason for this is that there is a strong relationship between the efficiency of inference and the actual storage model being used. Since any particular SAIL implementation has a complete understanding of the storage model (e.g. the database schema in the case of an RDBMS), this knowledge can be exploited to infer, for example, class subsumption more efficiently.
Another difference between SAIL and other RDF APIs is that SAIL is considerably more lightweight: only four basic interfaces are provided, offering basic storage and retrieval functionality and transaction support. This minimal set of interfaces promotes flexibility and looser coupling between components.
The current Sesame framework offers several implementations of the SAIL API. The most important of these is the SQL92SAIL, which is a generic implementation for SQL92, ISO99 [1]. This allows for connecting to any RDBMS without having to re-implement a lot of code. In the SQL92SAIL, only the definitions of the data-types (which are not part of the SQL92 standard) have to be changed when switching to a different database platform. The SQL92SAIL features an inferencing module for RDFS, based on the RDFS entailment rules as specified in the RDF Model Theory [2]. This inferencing module computes the closure of the data schema and asserts these implications as derived statements. For example, whenever a statement of the form (foo, rdfs:domain, bar) is encountered, the inferencing module asserts that (foo, rdf:type, property) is an implied statement. The SQL92SAIL has been tested in use with several DBMSs, including PostgreSQL8 and MySQL9 [3].
OWLIM is a high-performance semantic repository, implemented in Java and packaged as a Storage and Inference Layer (SAIL) for the Sesame RDF database. OWLIM is based on Ontotexts Triple Reasoning and Rule Entailment Engine (TRREE) - a native RDF rule-entailment engine. The supported semantics can be configured through the definition of rule-sets. The most expressive pre-defined rule-set combines unconstrained RDFS and OWL-Lite. Custom rule-sets allow tuning for optimal performance and expressivity. OWLIM supports RDFS, OWL DLP, OWL Horst, most of OWL Lite and OWL2 RL.
The two editions of OWLIM are SwiftOWLIM and BigOWLIM. In SwiftOWLIM, reasoning and query evaluation are performed in-memory, while, at the same time, a reliable persistence strategy assures data preservation, consistency, and integrity. BigOWLIM is the high-performance "enterprise" edition that scales to massive quantities of data. Typically, SwiftOWLIM can manage millions of explicit statements on desktop hardware, whereas BigOWLIM can manage billions of statements and multiple simultaneous user sessions.
The KRI in MOLTO uses BigOWLIM Version 3.3.
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| sesamearch.png | 115.61 KB |
3.1.3 OWLIM Interoperability and Architecture
OWLIM version 3.X is packaged as a Storage and Inference Layer (SAIL) for Sesame version 2.x and makes extensive use of the features and infrastructure of Sesame, especially the RDF model, RDF parsers and query engines.
Inference is performed by the TRREE engine, where the explicit and inferred statements are stored in highly-optimized data structures that are kept in-memory for query evaluation and further inference. The inferred closure is updated through inference at the end of each transaction that modifies the repository.
Figure 2 - OWLIM Usage and Relations to Sesame and TRREE
OWLIM implements the Sesame SAIL interface so that it can be integrated with the rest of the Sesame framework, e.g. the query engines and the web UI. A user application can be designed to use OWLIM directly through the Sesame SAIL API or via the higher-level functional interfaces such as RDFDB. When an OWLIM repository is exposed using the Sesame HTTP Server, users can manage the repository through the Sesame Workbench Web application, or with other tools integrated with Sesame, e.g. ontology editors like Protege and TopBraid Composer.
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| OWLIMarch.png | 233.19 KB |
3.1.4 The TRREE Engine
OWLIM is implemented on top of the TRREE engine. TRREE stands for "Triple Reasoning and Rule Entailment Engine". The TRREE performs reasoning based on forward-chaining of entailment rules over RDF triple patterns with variables. TRREEs reasoning strategy is total materialization, although various optimizations are used as described in the following sections.
The semantics used is based on R-entailment [4], with the following differences:
- Free variables in the head of a rule (without a binding in the body) are treated as blank nodes. This feature can be considered "syntactic sugar";
- Variable inequality constraints can be specified in the body of the rules, in addition to the triple patterns. This leads to lower complexity as compared to R-entailment;
- The "cut" operator can be associated with rule premises, the TRREE compiler interprets it like the "!" operator in Prolog;
- Two types of inconsistency checks are supported. Checks without any consequences indicate a consistency violation if the body can be satisfied. Consistency checks with consequences indicate a consistency violation if the inferred statements do not exist in the repository;
- Axioms can be provided as a set of statements, although those are not modeled as rules with empty bodies.
Further details of the rule language can be found in the corresponding OWLIM user guides. The TRREE can be con- figured via the rule-sets parameter, that identifies a file containing the entailment rules, consistency checks and axiomatic triples. The implementation of TRREE relies on a compile stage, during which custom rule-sets are compiled into Java code that is further compiled and merged in to the inference engine.
The edition of TRREE used in SwiftOWLIM is referred to as "SwiftTRREE" and performs reasoning and query evaluation in-memory. The edition of TRREE used in BigOWLIM is referred to as "BigTRREE" and utilizes data structures backed by the file-system. These data structures are organized to allow query optimizations that dramatically improve performance with large data-sets, e.g. with one of the standard tests BigOWLIM evaluates queries against 7 million statements three times faster than SwiftOWLIM, although it takes between two and three times more time to initially load the data.
3.1.5 Supported Semantics
OWLIM offers several pre-defined semantics by way of standard rule-sets (files), but can also be configured to use custom rule-sets with semantics better tuned to the particular domain. The required semantics can be specified through the rule-set for each specific repository instance. Applications, which do not need the complexity of the most expressive supported semantics, can choose one of the less complex, which will result in faster inference.
Pre-defined Rule-Sets
The pre-defined rule-sets are layered such that each one extends the preceding one. The following list is ordered by increasing expressivity:
empty: no reasoning, i.e. OWLIM operates as a plain RDF store;rdfs: supports standard RDFS semantics;owl-horst: OWL dialect close to OWL Horst; the differences are discussed below;owl-max: a combination of most of OWL-Lite with RDFS.
Furthermore, the OWL2 RL profile [5], is supported as follows:
owl2-rl-conf: Fully conformant except for D-Entailment, i.e. reasoning about data types;owl2-rl-reduced: As above, but with the troublesome prp-key rule removed (this rule causes serious scalability problems).
Custom Rule-Sets
OWLIM has an internal rule compiler that can be used to configure the TRREE with a custom set of inference rules and axioms. The user may define a custom rule-set in a *.pie file (e.g. MySemantics.pie). The easiest way to do this is to start modifying one of the .pie files that were used to build the pre-compiled rule-sets all pre-defined .pie files are included in the distribution. The syntax of the .pie files is easy to follow.
OWL Compliance
OWL compliance, OWLIM supports several OWL like dialects: OWL Horst [4], (owl-horst), OWL Max (owl-max) that covers most of OWL-Lite and RDFS, and OWL2 RL (owl2-rl-conf and owl2-rl- reduced).
With the owl-max rule-set, which is is represented in Figure 3, OWLIM supports the following semantics:
- full RDFS semantics without constraints or limitations, apart from the entailments related to typed literals (known as D-entailment). For instance, meta-classes (and any arbitrary mixture of class, property, and individual) can be combined with the supported OWL semantics;
- most of OWL-Lite;
- all of OWL DLP.
The differences between OWL Horst [4], and the OWL dialects supported by OWLIM (owl-horst and owl-max) can be summarized as follows:
- OWLIM does not provide the extended support for typed literals, introduced with the D*-entailment extension of the RDFS semantics. Although such support is conceptually clear and easy to implement, it is our understanding that the performance penalty is too high for most applications. One can easily implement the rules defined for this purpose by ter Horst and add them to a custom rule-set;
- There are no inconsistency rules by default;
- A few more OWL primitives are supported by OWLIM (rule-set
owl-max). These are listed in the OWLIM user guides; - There is extended support for schema-level (T-Box) reasoning in OWLIM.
Even though the concrete rules pre-defined in OWLIM differ from those defined in OWL Horst, the complexity and decidability results reported for R-entailment are relevant for TRREE and OWLIM. To put it more precisely, the rules in the owl-host rule-set do not introduce new B-Nodes, which means that R-entailment with respect to them takes polynomial time. In KR terms, this means that the owl-horst inference within OWLIM is tractable.
Inference using owl-horst is of a lesser complexity compared to other formalisms that combine DL formalisms with rules. In addition, it puts no constraints with respect to meta-modeling.
The correctness of the support for OWL semantics (for those primitives that are supported) is checked against the normative Positive- and Negative-entailment OWL test cases [6]. These tests are provided in the OWLIM distribution and documented in the OWLIM user guides.
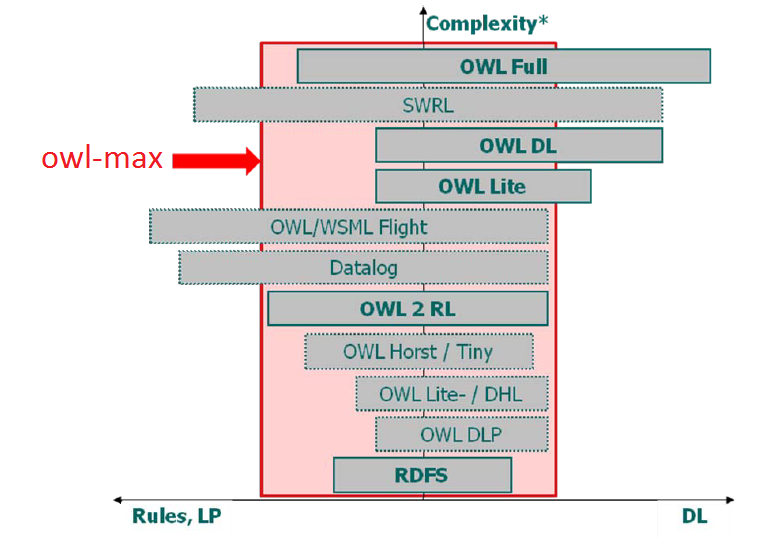
Figure 3 - Owl-max and Other OWL Dialects
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| owlmax.png | 207.68 KB |
3.2 RDFDB
The RDFDB stores all knowledge artifacts - such as ontologies, knowledge bases, and other data if available - in the RDF form. It is the MOLTO store and query service. The RDFDB has the following features:
- Default repository for structured data, which uses ORDI-SG integration layer over OWLIM – the fastest and most scalable Sesame Sail implementation;
- Storage and query APIs for the default repository, accessible over JMS;
- Storage and query APIs for the default repository, accessible through Sesame HTTP Server on port 9090.
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| ordi.png | 28.05 KB |
3.2.1 Overview
Using the RDF model to represent all system knowledge allows an easy interoperability between the stored data and the conceptual models and instances. Therefore, if the latter are enriched, extended or partially replaced, it is not necessary to change the implementation considerably. However, the requirements for tracking of provenance, versioning and stored knowledge meta-data make the use of RDF triples insufficient. Therefore, we use RDF quintuples and a repository model that supports them.
We will expose an open API, based on the ORDI SG data model that can be implemented for integration with alternative back-ends. The ORDI SG model is presented here in further detail, as it is the basis for the RDFDB API.
The atomic entity of the ORDI SG tripleset model is a quintuple. It consists of the RDF data type primitives - URI, blank node and literal, as follows:
{P, O, C, {TS1, ..., TSn}, where:
- S is the subject of a statement; of the type URI or blank node;
- P is the predicate of a statement; of the type URI;
- O is the object of a statement; of the type URI, blank node or literal;
- C is the context of a statement (i.e. Named Graph); of the type URI or blank node;
- {TS1, ..., TSn} is an unordered set of identifiers of the triplesets to which the statement is associated; of the type URI or blank node.
The ORDI data model is realized as a directed labeled multi-graph. For backward compatibility with RDF, SPARQL and other RDF-based specifications, a new kind of information is introduced to the RDF graph. The tripleset model is a simple extension of the RDF graph enabling an easy way for adding meta-data to the statements.
It is a new element in the RDF statement, previously expressed as a triple or a quadruple, to describe the relation between the statement and an identifiable group of statements. This new term is introduced to distinguish the new model from several similar, already existing, RDF extensions and the terms associated with them:
- Context, as defined in several RDF APIs like Sesame 2.0, YARS and others;
- Datasets, as defined in SPARQL;
- Named-graphs, as introduced at http://www.w3.org/2004/03/trix/, implemented in Jena and used in SPARQL.
The following is true for the tripleset model:
- Each contextualized triple {S, P, O, C} could belong to multiple triplesets;
- The triples are not "owned" by the contexts; a triple can be disassociated from a tripleset without being deleted;
- When a triple is associated with several triplesets it should be counted as a single statement, e.g. a single arc in the graph;
- A tripleset can contain triples from different contexts;
- Each tripleset can be converted to a multi-set of triples, as one triple can correspond to multiple contextualized triples, belonging to the tripleset.
Figure 4 below is a diagram of the relationship between the major elements in the ORDI data model.
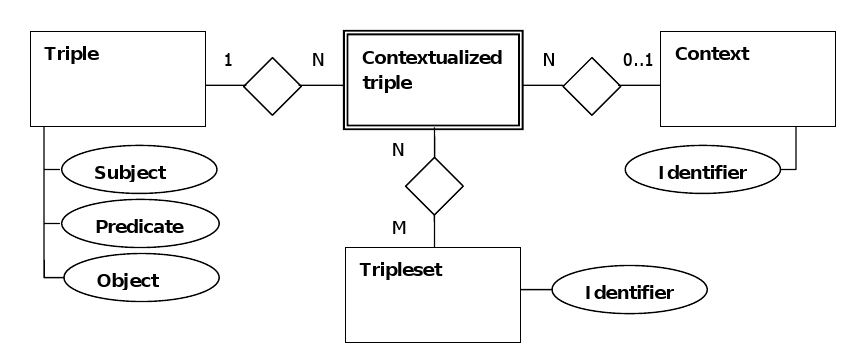
Figure 4 - Entity-Relationship Diagram of the ORDI Data Model
3.2.2 RDFDB Use
The RDFDB service is already available in the distribution and one could use it either by generating a JMS client or through the OpenRDF Sesame API.
Using the RDFDB by Generating a JMS Client
Generating a Client
Using your shell, navigate to the bin directory of the deployed platform and invoke the following commands:
mkproxy -proxy com.ontotext.platform.qsg.ServiceClass $PATH_TO_EXAMPLES/target/classes/
mkproxy -client com.ontotext.platform.qsg.ServiceClass $PATH_TO_EXAMPLES/target/classes/
Both commands dump output to sysout. Get the code, clean it as appropriate and put it in your project's source code. Build the project and the client is located in your project's target directory. The client implements the interface of the service.
Generating RDF-DB Clients
In order to use RDF-DB clients, the following services must be generated:
com.ontotext.rdfdb.ordi.OrdiService
com.ontotext.rdfdb.ordi.RdfStoreService
com.ontotext.rdfdb.ordi.RdfQueryService
Using the RDFDB through the OpenRDF Sesame API
By using the OpenRDF Sesame API one could manage and query the default repository through the Sesame Workbench, or operate over it using the HTTP Repository. The OpenRDF Sesame is integrated in the RDFDB. For more details about how to use it, please see the OpenRDF Sesame User Guide.
3.3 Data Sources
This section describes the conceptual models, ontologies and knowledge bases, used in the MOLTO KRI as a context background in the RDFDB component.
- PROTON ontology - a lightweight upper-level ontology defining about 300 classes and 100 properties in OWL Light.
- The default KRI knowledge base - common world knowledge that contains information about people, organizations, locations, and job titles.
Most applications of the KRI require extending the conceptual models with domain ontologies and the underlying knowledge base with domain specific entities and facts.
3.3.1 PROTON Ontology
PROTON ontology provides coverage of the most general concepts, with focus on named entities (people, locations, organizations) and concrete domains (numbers, dates, etc.).
The design principles can be summarized as follows:
- domain-independence;
- light-weight logical definitions;
- alignment with popular standards;
- good coverage of named entities and concrete domains (i.e. people, organizations, locations, numbers, dates, addresses).
The ontology is originally encoded in a fragment of OWL Lite and split into four modules: System, Top, Upper, and KM (Knowledge Management), shown on Figure 5 below.
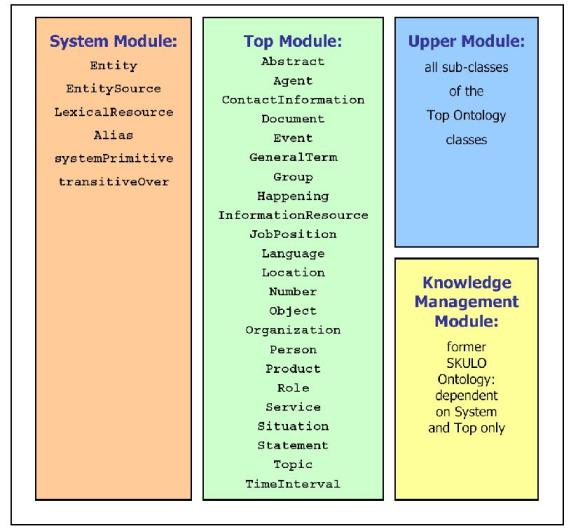
Figure 5 - PROTON Ontology
System module
The System module consists of a few meta-level primitives (5 classes and 5 properties). It introduces the notion of 'entity', which can have aliases. The primitives at this level are usually the few things that have to be hard-coded in ontology-based applications. Within this document and in general, the System module of PROTON is referred to via the "protons:" prefix.
Top module
The Top module is the highest, most general, conceptual level, consisting of about 20 classes. These ensure a good balance of utility, domain independence, and ease of understanding and usage. The top layer is usually the best level to establish alignment to other ontologies and schemata. Within this document and in general, the Top module of PROTON is referred to via the "protont:" prefix.
Upper module
The Upper module has over 200 general classes of entities, which often appear in multiple domains (e.g. various sorts of organizations, a comprehensive range of locations, etc.). Within this document and in general, the Upper module of PROTON is referred to via the "protonu:" prefix.
Knowledge Management (KM) module
The KM module has 38 classes of slightly specialized entities that are specific for typical Knowledge Management tasks and applications. Within this document and in general, the PROTON KM module is referred to via the "protonkm:" prefix.
3.3.2 The Default KRI Knowledge Base
The default KB contains numerous instances of PROTON Upper Module classes like: Public Company, Company, Bank, IndustrySector, HomePage, etc. It covers the most popular entities in the world such as:
- Locations: mountains, cities, roads, etc.
- Organizations, all important sorts of: business, international, political, government, sport, academic, etc.
- Specific people
Content
- collected from various sources, like geographical and business intelligence gazetteers
- predefined - KRI uses entities only from trusted sources
- can be enriched, replaced
Entity Description
The NE-s are represented with their Semantic Descriptions via:
- Aliases (Florida & FL);
- Relations with other entities (Person hasPosition Position);
- Attributes (latitude & longitude of geographic entities);
- the proper Class of the NE
The last build of the KRI KB contained 29104 named entities: 6006 persons, 8259 organizations, 12219 locations and 2620 job titles.
3.4 KRI Web UI
Although the KRI presented in this document comes directly from preexisting products that have not been developed specially for the needs of the MOLTO project, it provides the basic semantic functionality required by some MOLTO-specific applications. As an illustration, we present the following screen-shots of the KRI web UI. It allows the user to enter a natural language query, as shown in Figure 6. The natural language query is converted into a SPARQL query and the SPARQL query is executed by OWLIM through the RDFDB layer.
The conversion of the natural language query into a SPARQL query is out of the scope of this document, but will be described in details in Deliverable 4.3 Grammar-Ontology Interoperability.
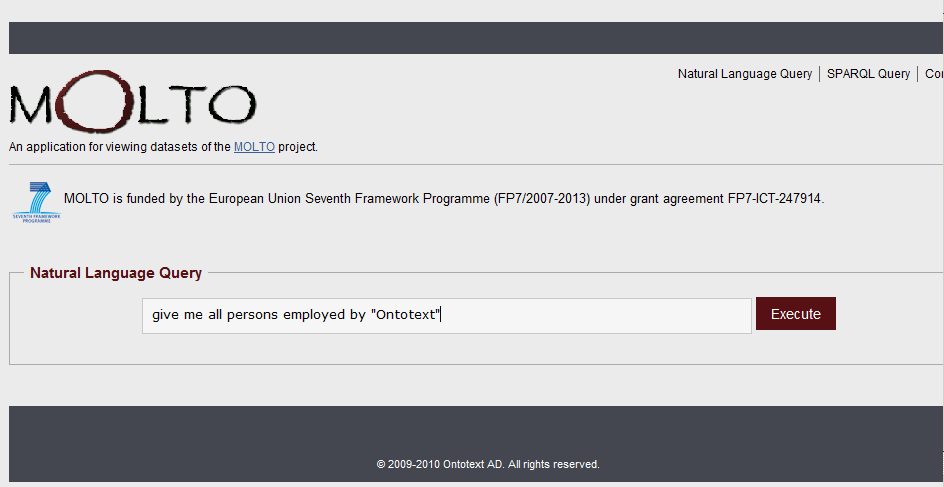
Figure 6 - Natural Language Query
The web UI shows the results of the executed SPARQL query, as shown in Figure 7 below.
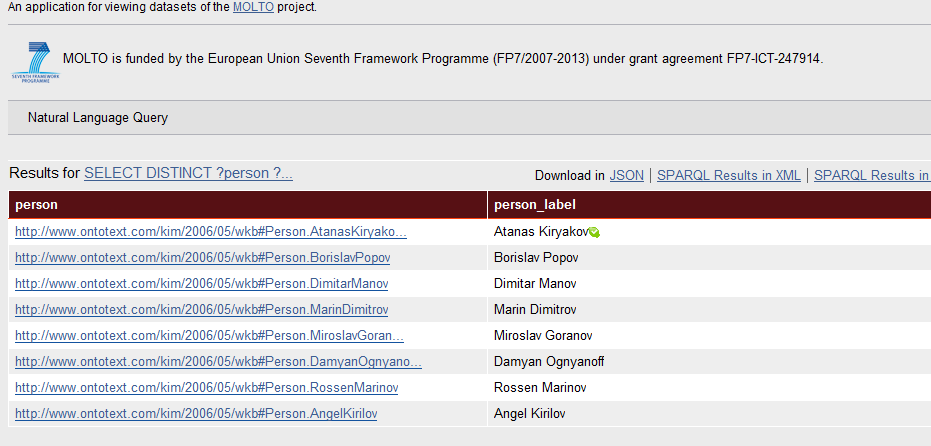
Figure 7 - Results from the SPARQL Query
The user can see and edit the SPARQL query or enter a new SPARQL query. The KRI web UI also gives the user the possibility to browse the underlying ontology and database.
| Attachment | Size |
|---|---|
| nlq.png | 26.84 KB |
| results.png | 36.41 KB |